
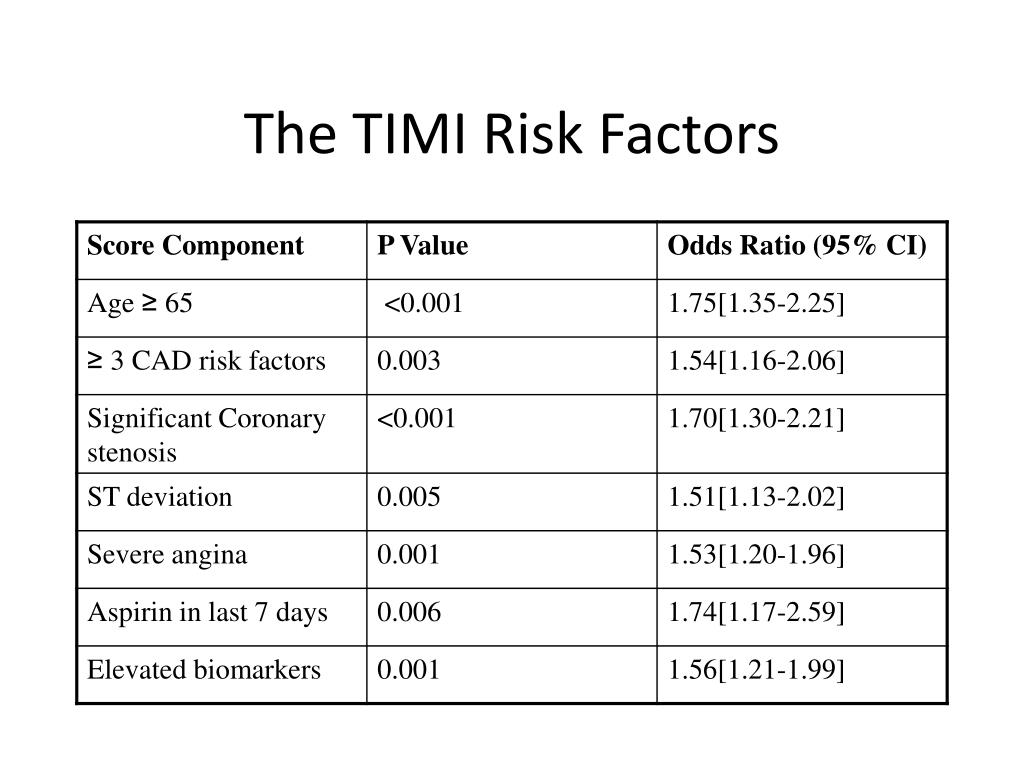
If an initial conservative strategy is selected and patient has recurrent ischemic discomfort with clopidogrel, ASA, and anticoagulant therapy, it is reasonable to add a GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor before diagnostic angiography. Either an IV GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor ( Level A) or clopidogrel ( Level B) should be added to ASA and anticoagulant therapy before diagnostic angiography. If an initial conservative strategy is selected and recurrent symptoms/ischemia, heart failure, or serious arrhythmias subsequently appear, then diagnostic angiography should be performed. noninvasive) strategy is selected, clopidogrel should be added to ASA and anticoagulant therapy as soon as possible after admission. Clopidogrel ( Level A) if not started beforehand. Otherwise during PCI one of the following:. An IV GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor ( Level A) preferably eptifibatide or tirofiban. Medium/High risk patients in whom initial invasive strategy is planned should receive dual therapy (Level A) including aspirin (Level A) and:. Clopidogrel loading dose should be initiated as soon as possible in patients unable to tolerate aspirin. Aspirin should be initiated as soon as possible and continued indefinitely in patients who tolerate it. Unstable Angina - NSTEMI Guidelines Summary of Class I Guidelines Those with recent MI (especially anterior) and LV dysfunction benefit most. Start short-acting ( captopril) within 24 hours of admission. Use diltiazem if cannot use beta-blocker ( nifedipine clearly harmful). Decreases inotropic and chronotropic response to catecholamines. #A TIMI RISK SCORE TRIAL#
ESSENCE trial showed 20% decrease in death, MI or urgent revascularization with LMWH. AHA recommends for moderate & high risk Unstable angina/NSTEMI unless CABG within 24hr. Give heparin or enoxaparin along with ASA (Class 1A evidence). Administer at time of PCI, not in the ED. Benefit only for patients undergoing PCI. Main risk and contraindication is bleeding. Mortality benefit with NSTEMI (CURE trial: Decrease in cardiovascular death, MI, or stroke by 9.3-11.5%). Clopidogrel (see drug link for specific age and indication-related dosages). In pts with true ASA allergies, substitute Clopidogrel. Should be used in all ACS unless contraindicated (eg Anaphylaxis). Medical management vs cath determined by level of risk for future cardiovascular events. Dual antiplatelet therapy and antithrombotic therapy is mainstay of treatment. High-risk findings on noninvasive stress testing. New or presumably new ST-segment depression. Recurrent angina/ischemia with or with out symptoms of CHF. Esophageal perforation (Boerhhaave's syndrome). More likely to report central chest painįactors associated with delayed presentation ĭifferential Diagnosis Chest pain Critical. More likely to report fatigue, dyspnea, indigestion, nausea or vomiting, palpitations, or weakness, although some studies have found fewer differences in presentation. Less likely to receive timely reperfusion therapy. 
Less likely to undergo cardiac catheterization.Less likely to be treated with guideline-directed medical therapies.Chest pain associated with nausea/vomitingĬlinical factors that decrease likelihood of ACS/AMI:.
 Chest pain radiating to both arms > R arm > L arm. Type 5: Myocardial Infarction Related to CABG ProcedureĬlinical factors that increase likelihood of ACS/AMI:. Type 4: Myocardial Infarction Associated With Revascularization Procedure. Sudden cardiac death with symptoms suggestive of myocardial ischaemia without elevated biomarkers. Type 3: Cardiac Death Due to Myocardial Infarction. coronary spasm, embolism, low or high blood pressures, anemia, or arrhythmias) Condition other than CAD contributes to an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and/or demand (e.g. Type 2: Myocardial Infarction Secondary to an Ischemic Imbalance. Atherosclerotic plaque rupture or intraluminal thrombus in one or more of the coronary arteries. Type 1: Spontaneous Myocardial Infarction.
Chest pain radiating to both arms > R arm > L arm. Type 5: Myocardial Infarction Related to CABG ProcedureĬlinical factors that increase likelihood of ACS/AMI:. Type 4: Myocardial Infarction Associated With Revascularization Procedure. Sudden cardiac death with symptoms suggestive of myocardial ischaemia without elevated biomarkers. Type 3: Cardiac Death Due to Myocardial Infarction. coronary spasm, embolism, low or high blood pressures, anemia, or arrhythmias) Condition other than CAD contributes to an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and/or demand (e.g. Type 2: Myocardial Infarction Secondary to an Ischemic Imbalance. Atherosclerotic plaque rupture or intraluminal thrombus in one or more of the coronary arteries. Type 1: Spontaneous Myocardial Infarction.  NSTEMI includes Type 2 -Type 5 biomarker elevations. Association between quantity of troponin and risk of death. Age >65 with MI and anemia had 33% reduction in 30 day mort if transfused to keep HCT >30. 5% of NSTEMI will develop Cardiogenic Shock (60% mortality). 33% with confirmed MI have no chest pain on presentation (especially older, female, DM, CHF).
NSTEMI includes Type 2 -Type 5 biomarker elevations. Association between quantity of troponin and risk of death. Age >65 with MI and anemia had 33% reduction in 30 day mort if transfused to keep HCT >30. 5% of NSTEMI will develop Cardiogenic Shock (60% mortality). 33% with confirmed MI have no chest pain on presentation (especially older, female, DM, CHF). 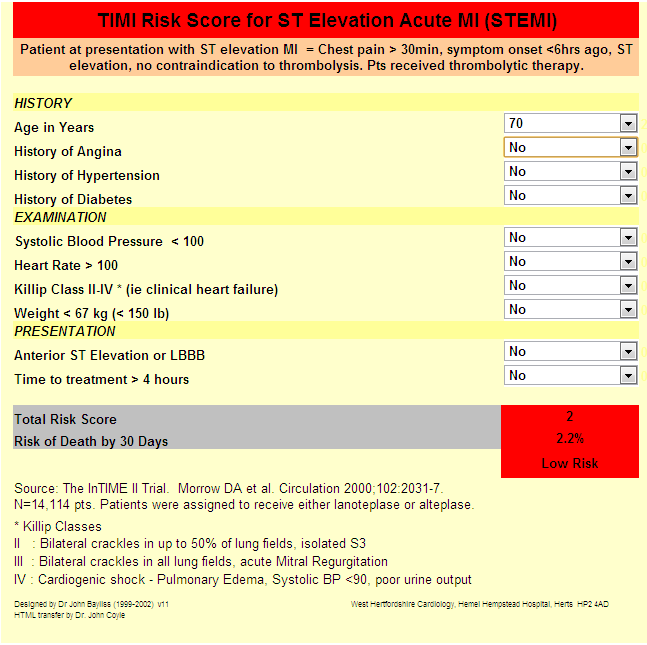
5.4 Unstable Angina - NSTEMI Guidelines.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
